Simple Example
By leveraging Job Submission, users can run jobs (such as a time-consuming ML training) in the background while doing other analyses in JupyterLab at the same time.
In this tutorial, we are going to demonstrate the usage of a job submission with a simple example.
Prerequisite
Group Volume
To fully utilize all Job Submission functions, there must be a group volume in your group. If you do not have one, please ask your administrator to create one for you.
Jobs cannot access user volume and a job's working directory is also a temporary directory. Therefore, the easiest way to persist your outputs is to output them into group volume. Also, the easiest way to use the code written in JupyterLab is to put your code in group volume.
The rest of this tutorial assumes that you have group volume.
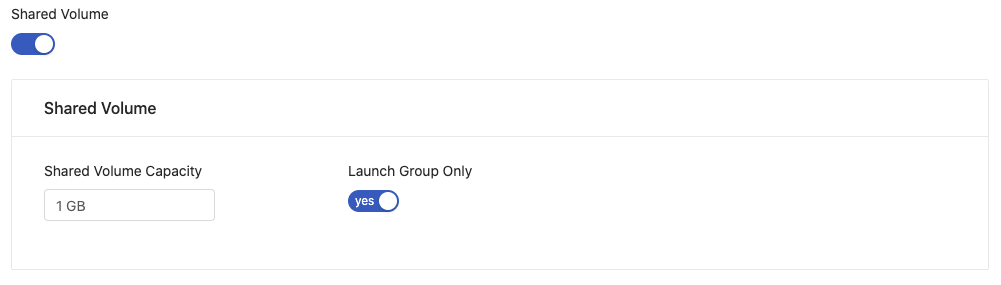
Ask your administrator to switch on shared volume in Groups tab under the Admin page
Image and Instance Type
This tutorial uses minor computing resources (CPU: 0.5 / Memory: 1G / GPU: 0) and jupyter/base-notebook.
Please make sure you have this kind of image and instance type. If not, please also submit a request to your administrator to create these for you in the Admin page.
Group Quota and User Quota
For this tutorial, the necessary total quota is two virtual CPU and 4GB RAM. Please ensure that you have enough quota or contact your administrator.
Tutorial Steps
We are going to run this code below as a job, in order to run the code successfully, the python package camelcase is necessary; camelcase is a tool which provides a method capitalizes the first letter of each word.. By using it, this code will output capitalized This Method Capitalizes The First Letter Of Each Word. every 1s 10 times in total.
import time
import camelcase
camel = camelcase.CamelCase()
txt = "this method capitalizes the first letter of each word."
start = 1
end = 10
print("Counting from 1 to 10:")
for num in range(start, end + 1):
time.sleep(1)
print('{}: {}'.format(num, camel.hump(txt)))
Login
PrimeHuband selectNotebook.Select an
instance typeand animagefor launching a Notebook.Double click your group volume folder for entering it.
Click
Text Filein the right hand side under the 'Other' section.Right click on the new
untitled.txtand rename it intointerval.py.Input the code above and save.
We have created a python file for our coming job. We can shutdown the Notebook or leave it. Next we are going to run it as a job.
Submit a Job
Confirm if the current group is what you desire; switch the group by the Group: dropdown at the top of the right side.
Open
Jobsfrom portal and and create a job.Select your instance type and image on the left panel; ensure that these are the identical to the ones you are using in JupyterLab.
In the right panel, name the job
countingin Job Name input field, or another name that prefer.Since our code is under group volume and will be mounted in
/home/jovyan/<group name> -> /project/<group name>, type the following into the Command input field; replace<group name>.<group name>is case sensitive; [REF] Directories/Paths.We use
camelcasepackage in the code, it has to be installed first before code execution.pip install camelcase cd /project/<group name>/ python -u interval.py
Some notes for the Command input field:
- You need to
cdinto<group name>first. Because we save model in a relative path. <group name>is case sensitive;- You may notice there is a
-uin python command. In Job Submission, Python will buffer the log by default. Adding-utells Python not to buffer the log so that we can see the log in real time. - Job Submission will execute command column as a shell script. Therefore, you can write multiple line just like you are writing a shell script.
- If you hover your mouse over the question mark next to
Command, you can see more hints.
- Submit the job, then status of job is changed from pending to running.
Jobs List and Refresh Button
Once a jub is submitted, the intial status is Pending. Clicking the Refresh button to update the status.
Logs Tab
Once the job succeeded, we should see the similar log, and we can tell the job installed python package camelcase first, then entering the group volume and run interval.py.

Congratulations, we have submitted a code as a job and run it successfully and we learnt how to interact files in group volume from a command field of a job.